The Redheaded Stepchild
 Mon, March 9, 2020
Mon, March 9, 2020 
Cyclists have always been society’s “Redheaded Stepchild;” unloved and abused throughout history. The above picture is titled, "The Unrestrained Demon of the Wheel,” published in “The Judge,” Sept. 23, 1893, reflects the attitude of the day.
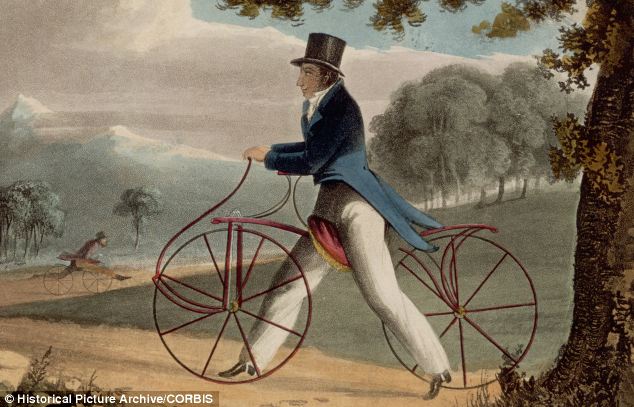
Since the invention of the ordinary, or high-wheeler in the late 1800s, when horse drawn carriages were the transport of the day. It was the wealthy classes who owned carriages, and bicycles scared the horses.
It was not uncommon for a coach driver to lash out at a passing cyclist with his horsewhip, and pedestrians were not above putting a walking stick through a rider’s wheel.
Bicycles were expensive and initially cycling was a sport of the wealthy, but it was a young man’s pastime and even wealthy young men were viewed with disdain by the older generation.
Cycling was initially banned in places in England as being too dangerous. However, being a “rich man’s sport,” the ban was short lived. By 1880 there were 213 established cycling clubs in the UK. Remember, this was before the invention of the “Safety Bicycle” in 1885, and the pneumatic tire in 1888.
With the invention of the “safety” bicycle, and mass production that followed, it really changed the face of the sport, and people’s attitude to it. Cycling became affordable to the working classes and it quickly became both a pastime and a mode of transport of the masses.
In England the wealthy who lived on large country estates, suddenly found their space invaded on the weekends by the working classes on their bicycles as they ventured outside the cities for the first time to explore the countryside.
Cycling was no longer a pastime for the wealthy, in fact to ride a bicycle was now a definite sign of being lower class.
The privileged upper classes looked for new ways to reclaim the highways again; of course, they found it in the form of the automobile.
However, the resentment towards cyclists, by the upper classes, was already established long before the automobile arrived.
The invention of the pneumatic tire meant there was an explosion in the sport of cycle racing. And nothing will disrupt a quiet Sunday drive to church by the local gentry, like a bike race. This led to a ban in England of mass start road racing in 1894; a ban that would last until the 1950s.
The result was road racing never developed in the UK as it did in the rest of Europe. In countries like France, Holland, Belgium, and Italy cyclists receive respect and toleration because of the popularity of cycle road racing in those countries. The general public on the continent of Europe has become used to seeing cyclists racing and training on the highways.
The only competitive events open to British cyclists were track racing, of course limited to those close to a track. A few mass start circuit races in private parks, and individual time trials, which would become the mainstay of British cycling competition.
It is interesting to note that in 1894, as road racing was banned in England as being too dangerous; the first motor race was held on public roads in France. This led to almost ten years of absolute carnage as racecars quickly developed to reach speeds of 100 mph (Without the brakes, steering and road surfaces to match these speeds.) and there was wholesale slaughter of both spectators and drivers.
The attitude of the wealthy was no doubt one of, what were the deaths of a few of the peasant class, as long as they could enjoy their sport? Much the same state of affairs existed in the United States; it was the privileged who initially drove cars. They set the rules of accepted behavior and attitudes, which still exist today.
Is this not still the attitude now? “What is the death or injury of a few, as long as I can drive as fast as I like, and in a manner that suits me?” Of course, no one intends for people to die, but behave in a certain way and the inevitable will happen. And if a cyclist or pedestrian gets hit, no real concern, just the question, “What were they doing on the road anyway?”
When Henry Ford made cars available to the masses, naturally they expected to drive to the same standards set by their wealthy predecessors. All road safety legislation since has been aimed at protecting the person inside the car, with little thought going into the protection of other road users, namely pedestrians and cyclists.
Those of us today exercising our rights by riding our bike on the public highways should not despair. However, we should be realistic and recognize that current attitudes of the general public have been formed over a 100 years, or more; change will continue, but slowly.
In the mean time we will remain the Redheaded Stepchild, and should expect the abuse to continue until further notice..






















Progress
I first got into bike racing at the age of 16, in 1952. To the present day as I write, that is 67 years of racing bikes, studying and writing about bikes, and designing and building bikes. Looking back over this period, there were very few technological changes in the first thirty years from the 1950s to the 1980s.
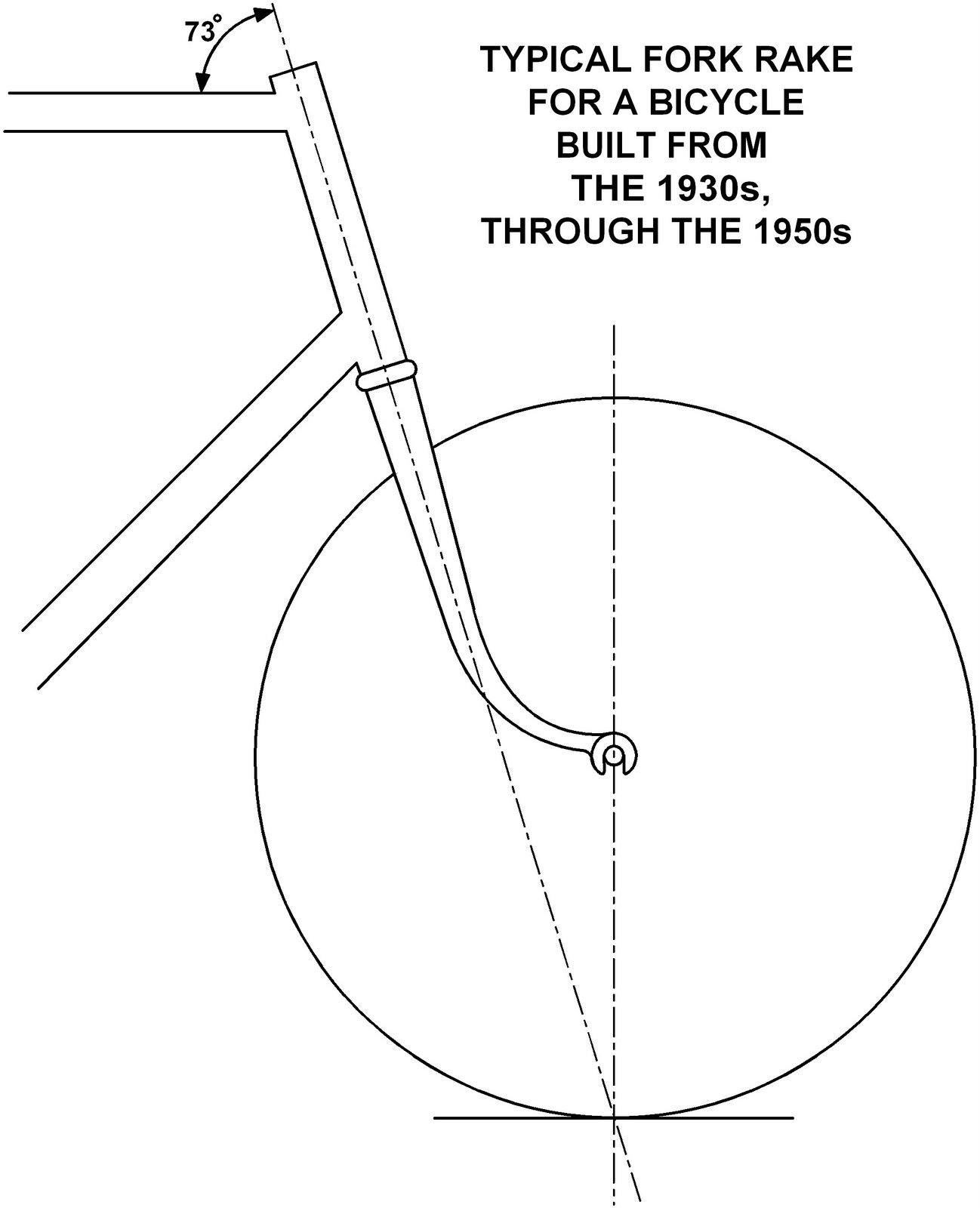
Frames were brass brazed, lugged steel, built by craftsmen. With standard size steel tubes as they had been for fifty years prior to that. All had level top tubes, it was the framebuilder’s point of reference. An individual could establish his frame size, and after that could buy any make of frame in that size, and it would fit.
There were subtle changes in racing frame geometry, but not so much that all but the most avid bike enthusiast would even know about, and apart from that we went from 5 speed to 6 speed and that was it.
However, in the next thirty or more years that followed, from the 1980s to the present day, the bicycle has changed at an alarming rate, as has technology in general. The mountain bike, indexed gear shifting, which lead to 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 speed, clipless pedals and Carbon fiber frames.
For more than thirty years all professional cyclists and almost all amateur cyclists used Christophe steel toe clips and Binda toe straps. It was a common standard of excellence. Then in the late 1980s clipless or clip in pedals appeared and in a few short years toe clips and straps were obsolete.
That is progress, and yes I will agree it is an improvement, but imagine how the owners of Christophe and Binda must have felt seeing their lucrative business as the major suppliers of toe clips and straps for the entire world, disappear in a very short period of time.
What has changed is not only the bicycle itself, but the whole structure of the bicycle industry. Individual craftsmen are now obsolete. Racing bicycles are produced by a few large corporations worldwide. Individual craftsmen were content to make a good living wage, which probably accounts for the lack of progress in the first thirty years I speak of.
This can be viewed as a good or bad thing, but bicycle racing is a simple sport and requires a simple machine to participate. Individual builders like myself in the UK and the rest of Europe catered almost exclusively to amateur racing cyclists. Everyone wanted to emulate the professional cyclists, and use whatever they were riding.
Everything changed in the 1970s with the “Bike Boom” in America. A few die hard enthusiasts wanted what the pros rode. But to the general American public, the race bike was over geared and very uncomfortable to ride. This is why the Mountain Bike became a huge hit in the 1990s, more comfortable, and easier to ride.
It used to be, “What the Pros rode” that drove the market. Today it is the American leisure market that drives the Industry, and the pros ride what the corporations who sponsor them, tell them to ride. A wider range of gears, is probably the single most technological improvement that has benefited professional cycling.
Disc brakes being forced on the pros is a prime example of unwanted and unnecessary technology that complicates a fast wheel change that is vital in pro cycling. However, for the corporations it creates built in obsolescence so necessary to create continued sales.
Professional Cycling is harder and more demanding than many other sports, and in many cases less rewarding financially. What makes the sport unique is the fact that one rider can draft behind another, making the cycle racing highly tactical as well as physical. It is what makes the sport unpredictable, and exciting to watch. No amount of technology will ever change this.